Are you contemplating the installation of a car lift in your garage? Before taking the plunge, it’s crucial to understand the electrical requirements for safe and efficient operation. A grasp of your car lift’s electrical demands can help you steer clear of potential electrical hazards and costly repairs.
Most car lifts necessitate a 220-volt power source with an amp rating ranging from 15 to 50 amps. The exact amp requirement hinges on factors such as the lift’s weight capacity, lifting height, and motor power. Additionally, proper amperage breakers and wiring are imperative for the lift’s safety and to mitigate the risk of electrical fires.
In this discussion, we’ll explore the typical amp prerequisites for various car lifts, the recommended breaker size for a 2-post car lift, and the consequences of employing an incorrect amp power unit. Let’s delve into the world of car lift amperage.
Understanding the Amps Required by a Car Lift
The electrical amp requirement of a car lift is contingent on its type:
For a 4-Post Car Lift:
- A 4-post commercial-grade auto lift, featuring a 220 Volt single-phase motor, mandates a minimum of 30 amps of service and necessitates 10-gauge wiring. This robust lift is designed for heavy-duty use in professional garage settings, capable of elevating larger vehicles with enhanced stability.
- Conversely, if you have a 4-post hobbyist lift, a 110 Volt grounded power supply with 30 amps service is sufficient. This lift type is tailored for personal use in a home garage or a small workshop.
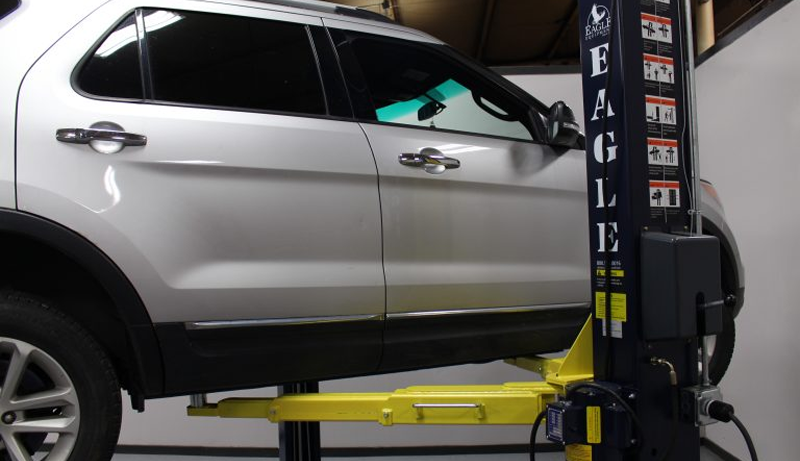
For a 2-Post Car Lift:
- A 220 Volt single-phase car lift motor typically requires an amp service ranging from 14.5 to 16.5 amps. It’s essential to confirm that your electrical system can handle this load. Upgrading from a standard 15-amp outlet to a 20-amp GFCI outlet can enhance safety and ensure your lift operates without electrical hazards.
An unreliable car lift can pose serious safety risks, especially when working alone in your garage with a vehicle suspended in the air.
Typical Amp Requirement for Most Car Lifts
Car lifts tend to draw significant electricity, usually falling within the 15 to 25 amp range. This heightened electrical consumption is necessary due to the torque needed to safely elevate heavy vehicles. The motor must generate ample power to facilitate smooth and controlled lifting, minimizing abrupt jerks or unexpected movements.
It’s imperative to ensure that your electrical system can accommodate your car lift’s amp requirement. Insufficient power provision may lead to improper lift operation or even potential damage.
Choosing the Right Breaker Size for a 2-Post Lift
For a 2-post lift, the recommended breaker size is 30 amps. This ensures that your lift receives the requisite power to operate effectively while reducing the risk of accidents or damage to your electrical system.
Consequences of Incorrect Amp Power Unit Usage
Employing an inappropriate amp power unit for your car lift can result in numerous complications. Inadequate electrical power can cause the lift to operate sluggishly or not function at all, while overloading can damage critical lift components.

Here are some potential consequences:
Insufficient Power:
- When the amp power unit fails to meet the lift’s requirements, the lift may operate slowly, struggle to reach desired heights, or fail to work altogether. Insufficient power can strain the lift, leading to sluggish movements and difficulties in lifting heavy cars or achieving higher elevations.
- Furthermore, if the power unit lacks the necessary strength, it poses a safety hazard, as the lift may fail or collapse under the vehicle’s weight. Ensuring the amp power unit aligns with the lift’s requirements is vital to prevent accidents or damage.
Overloading:
- Overloading the amp power unit of the car lift is not only ineffective but also poses a risk of severe damage to the vehicle. It places undue stress on the lift’s components, potentially resulting in mechanical failure or even collapse.
Given that the power unit isn’t designed to handle loads exceeding the lift’s capacity, attempting to lift a vehicle beyond its limits may lead to malfunction.
Motor Damage
Using a car lift beyond its intended capacity can lead to motor overwork, causing overheating and premature wear. Such strain on the motor can result in costly repairs and operational downtime.
This excessive workload may lead to engine damage, overheating, and a reduced lifespan for the motor. In severe cases, the motor could fail completely, necessitating expensive repairs or a complete replacement.
Furthermore, this type of damage not only incurs significant costs but also poses a substantial safety risk. If the motor were to fail during operation, it could result in a sudden drop of the lift, potentially causing severe injuries or even fatalities.
Safety Hazards
Ensuring compatibility between your car lift and its power unit is crucial to avoid safety hazards. Inadequate amperage supply from the power unit can lead to unstable lifting, sudden descents, or unintended movements.
These risks not only jeopardize the operator’s safety but also pose a threat to the lifted vehicle and anyone in the vicinity. Incompatibility with the power unit can also cause malfunctions in the lift’s safety mechanisms, further increasing the likelihood of accidents.
Do Car Lifts Require a Dedicated Circuit?
To ensure the safe installation and operation of your car lift, it is imperative to have a dedicated circuit with either a time delay fuse or a double-pole circuit breaker rated at 25 amps. This dedicated circuit should exclusively serve the car lift and should not be shared with any other appliances or devices in your garage.
Car lifts demand a substantial amount of power to function properly, and sharing a circuit with other devices can lead to circuit overloads, creating potential safety hazards. Here’s why a dedicated circuit is necessary:
- Shared circuits may frequently trip the circuit breaker, causing frustration and delays.
- Sharing a circuit can compromise the stability and consistency of the power supply, potentially causing damage to the car lift and other appliances.
- In some instances, sharing a circuit may violate electrical codes and regulations, resulting in fines or legal actions.
Do I Need a Disconnect for a Car Lift?
In accordance with electrical code regulations, the installation of an automotive lifting device necessitates the presence of a disconnect device. This device is crucial for safety purposes, allowing the rapid and easy shutdown of the power supply to the lift in case of emergencies.
Here are key considerations regarding disconnect devices for car lifts:
- Electrical codes mandate the installation of a disconnect device for every automotive lifting device.
- The disconnect device should be situated within the operator’s line of sight and easily accessible.
- Selecting a disconnect device with the appropriate rating for the lift’s amperage and the power supply voltage is vital.
To ensure both operator and lift safety, it is essential to have a disconnect device installed in compliance with electrical code regulations.

Safely Power Your Car Lift: Determine Amp Requirements Now that you are aware of the standard amp requirements for most car lifts and the correct breaker size for a 2-post lift, remember that choosing the appropriate power amplification for your car lift is crucial to prevent serious consequences.
Additionally, it is recommended to provide your car lift with a dedicated circuit, avoiding the sharing of circuits with other appliances. The installation of a disconnect device for the car lift is also advisable for safety purposes. Ensure that all components are set up correctly to mitigate the risk of accidents or mishaps.
The Basics of Car Lifts
Before we dive into the electrical requirements, let’s briefly discuss the different types of car lifts commonly used in automotive facilities.
- Two-Post Lifts: These are the most common type of car lifts and are typically used for lifting cars and light trucks. They consist of two upright posts on either side of the vehicle and two arms that raise the car from the chassis.
- Four-Post Lifts: Four-post lifts are known for their stability and are often used for larger vehicles like trucks and SUVs. They have four posts, with a platform that the vehicle sits on top of. These lifts are also used for vehicle storage.
- Scissor Lifts: Scissor lifts are compact and versatile, making them suitable for both small garages and larger automotive shops. They use a scissor-like mechanism to lift the vehicle, making them ideal for undercarriage work.
- In-Ground Lifts: These lifts are installed flush with the garage floor and are typically used in commercial repair facilities. They offer unobstructed workspace and can handle heavy-duty vehicles.
Understanding the Electrical Requirements
The electrical requirements of a car lift can vary significantly depending on its design, capacity, and manufacturer. However, there are some common factors that can help determine how many amps a car lift uses:
- Motor Power: The primary source of electrical consumption in a car lift is the motor that drives the lifting mechanism. Lift motors are typically rated in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW). The higher the horsepower or kW rating, the more electrical power the motor will require. A typical car lift motor may range from 2 HP to 5 HP or more.
- Voltage: Car lifts are commonly available in 110V, 220V, or 440V versions, depending on their size and lifting capacity. The voltage level significantly impacts the amperage required. Lower voltage lifts will draw more amperage to achieve the same power output compared to higher voltage ones.
- Phase: Car lifts can be single-phase or three-phase. Three-phase motors are more energy-efficient and may require less amperage to operate compared to single-phase motors of the same power rating.
- Duty Cycle: The duty cycle of the lift motor also plays a role in determining its amperage usage. Continuous-duty motors are designed to run continuously without overheating and may require more power compared to intermittent-duty motors.
Calculating Amps
To calculate how many amps a car lift uses, you can use the following formula:
Amps = Power (Watts) / Voltage
For example, if you have a car lift with a 3 HP motor operating on 220V, you can calculate the amperage as follows:
Amps = (3 HP * 746 watts/HP) / 220V = 10.15 Amps
It’s important to consult the manufacturer’s specifications for your specific car lift to get the most accurate amperage requirement. Additionally, consider the other electrical devices and equipment in your garage to ensure your electrical supply can handle the combined load.
FAQ: How Many Amps Does a Car Lift Use?
What determines the amperage of a car lift?
The amperage of a car lift is primarily determined by the motor’s power rating (in horsepower or kilowatts), the voltage it operates on, its phase (single or three-phase), and its duty cycle.
Do all car lifts use the same amount of amps?
No, the amperage requirements vary between different types and models of car lifts. The amperage will depend on factors such as the lift’s design, size, and manufacturer specifications.
Are there different voltage options for car lifts?
Yes, car lifts are available in various voltage options, including 110V, 220V, and 440V. The voltage level significantly affects the amperage required for operation.
What is the significance of voltage in amperage usage?
The voltage level directly impacts the amperage. Lower voltage lifts will draw more amperage to achieve the same power output compared to higher voltage ones. It’s crucial to choose the appropriate voltage for your specific lift.
Are three-phase lifts more energy-efficient than single-phase lifts?
Yes, in general, three-phase motors are more energy-efficient than single-phase motors of the same power rating. They may require less amperage to operate, which can reduce energy consumption.
How can I calculate the amperage my car lift uses?
You can calculate the amperage using the formula: Amps = Power (in watts) / Voltage. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for the motor’s power rating and your lift’s voltage to get an accurate amperage figure.
What other factors should I consider regarding amperage usage in my garage?
When assessing amperage usage for your car lift, consider the combined electrical load of all the equipment in your garage, including lighting, air compressors, and other power tools. Ensure your electrical supply can handle the total load without overloading.
Is it essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for electrical requirements?
Yes, it is crucial to adhere to the manufacturer’s specifications for your car lift’s electrical requirements. This ensures safe and efficient operation, prolongs the lift’s lifespan, and prevents electrical issues.
Can I use an extension cord for my car lift if it’s far from the power source?
It is not recommended to use an extension cord for a car lift. Instead, it’s advisable to have a licensed electrician install the lift with the proper wiring and outlets to meet the manufacturer’s electrical requirements.
What precautions should I take when working with a car lift’s electrical system?
Always turn off the power supply before performing any maintenance or electrical work on the lift. If you’re not experienced with electrical systems, it’s best to hire a qualified electrician to handle any electrical issues or installations.
Conclusion
The number of amps a car lift uses depends on various factors, including motor power, voltage, phase, and duty cycle. Understanding these requirements is essential for safe and efficient operation. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications and consider your electrical infrastructure to ensure your car lift operates smoothly and reliably in your automotive facility. Proper electrical planning is crucial to keep your lift and other equipment running smoothly without overloading your electrical system.




Leave a Reply